实现简单的RPC(Remote procedure call)
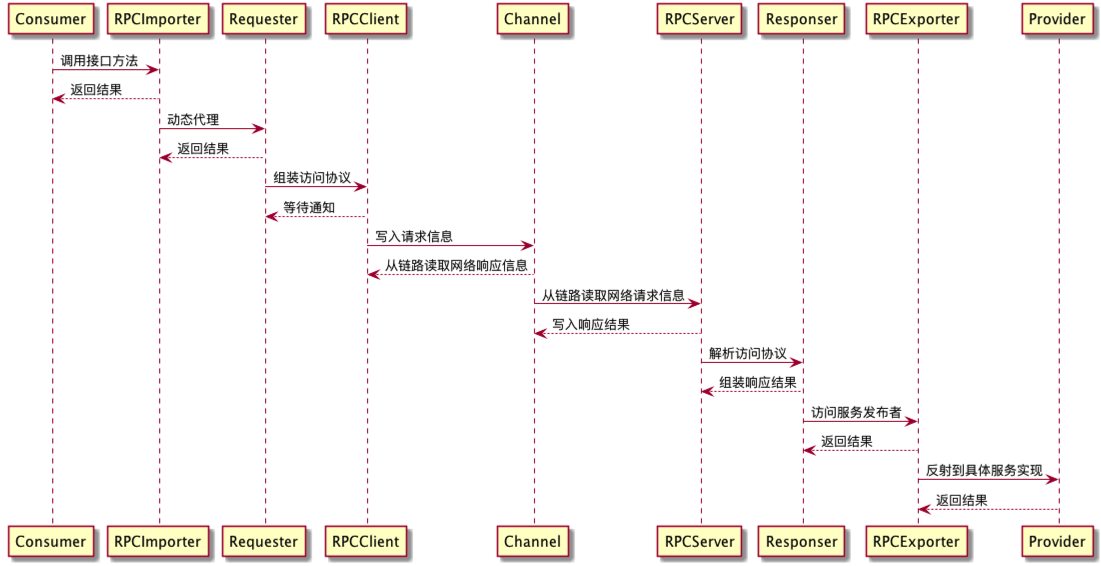
整体架构
代码实现
服务接口
| [EchoService] []
public interface EchoService {
String echo(String ping);
}
|
服务实现
1
2
3
4
5
6
| [EchoServiceImpl] []
public class EchoServiceImpl implements EchoService {
public String echo(String ping) {
return ping != null ? ping + " --> I am Ok." : "I am Ok.";
}
}
|
服务发布者(Exporter)
服务发布者
主要职责如下:
- 作为服务端,监听客户端TCP连接,接收到客户端连接后,将其封装成Task,由线程池执行
- 将客户端发送的码流发序列化成对象,反射调用服务实现者,获取执行结果
- 将执行结果对象反序列化,通过ocket发送给客户端.
- 远程服务调用完成之后,释放Socket等连接资源,防止句柄泄露
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
| [RpcExporter] []
public class RpcExporter {
static Executor executor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors());
public static void exporter(String hostname, int port) throws Exception {
ServerSocket server = new ServerSocket();
server.bind(new InetSocketAddress(hostname, port));
try {
while (true) {
executor.execute(new ExporterTask(server.accept()));
}
} finally {
server.close();
}
}
private static class ExporterTask implements Runnable {
Socket client = null;
public ExporterTask(Socket client) {
this.client = client;
}
public void run() {
ObjectInputStream input = null;
ObjectOutputStream output = null;
try {
input = new ObjectInputStream(client.getInputStream());
String interfaceName = input.readUTF();
Class<?> service = Class.forName(interfaceName);
String methodName = input.readUTF();
Class<?>[] paramterType = (Class<?>[]) input.readObject();
Object[] arguments = (Object[]) input.readObject();
Method method = service.getMethod(methodName, paramterType);
Object result = method.invoke(service.newInstance(), arguments);
output = new ObjectOutputStream(client.getOutputStream());
output.writeObject(result);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (output != null) {
try {
output.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (input != null) {
try {
input.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
}
}
if (client != null) {
try {
client.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
}
|
本地代理(Importer)
本地代理
主要职责如下:
将本地的接口调用转换成JDK动态代理,在动态代理中实现接口的远程调用
创建Socket客户端,根据指定地址连接远程服务提供者
将远程服务端调用所需的接口类,方法名,参数列表等编码后发送给服务提供者
同步阻塞等待服务端返回应答,获取应答之后返回
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
| [RpcImporter] []
public class RpcImporter<S> {
public S importer(final Class<?> serviceClass, final InetSocketAddress addr) {
return (S) Proxy.newProxyInstance(serviceClass.getClassLoader(), new Class<?>[]{serviceClass.getInterfaces()[0]}, new InvocationHandler() {
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
Socket socket = null;
ObjectOutputStream output = null;
ObjectInputStream input = null;
try {
socket = new Socket();
socket.connect(addr);
output = new ObjectOutputStream(socket.getOutputStream());
output.writeUTF(serviceClass.getName());
output.writeUTF(method.getName());
output.writeObject(method.getParameterTypes());
output.writeObject(args);
input = new ObjectInputStream(socket.getInputStream());
return input.readObject();
} finally {
if (socket != null) {
socket.close();
}
if (output != null) {
output.close();
}
if (input != null) {
input.close();
}
}
}
});
}
}
|
测试类
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
| [RpcTest] []
public class RpcTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Thread(new Runnable() {
public void run() {
try {
RpcExporter.exporter("localhost", 8080);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}).start();
RpcImporter<EchoService> importer = new RpcImporter<EchoService>();
EchoService echoService = importer.importer(EchoServiceImpl.class, new InetSocketAddress("localhost", 8080));
System.out.println(echoService.echo("Are you Ok?"));
}
}
|
